- Home
- Resources
- Patient Release Form to obtain your records from other Physician
- Patient Release Form to release your records to other Physician
- Insurance and Billing
- What should I bring to Appointments
- Glossary in English
- Glosarios de Examenes de diagnostico
- High School Sports Injuries
- Stretching Exercises for Sports
- Childhood Obesity and bone, joint & muscle health
- News
- Staff
- Conditions
- Galleries
- FAQ
- Zink Blog
- Contact
Broken Bones
Pediatric Broken Bones
What is a fracture?
A fracture is a partial or complete break in the bone. When a fracture occurs, it is classified as either open or closed:
- Open fracture (also called compound fracture). The bone exits and is visible through the skin, or a deep wound that exposes the bone through the skin.
- Closed fracture (also called simple fracture). The bone is broken, but the skin is intact.
Fractures have a variety of names. Below is a listing of the common types that may occur in children:
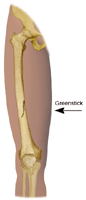
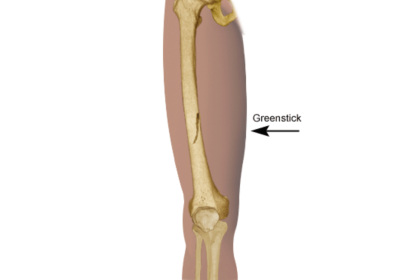
- Greenstick. Incomplete fracture. A portion of the bone is broken, causing the other side to bend.
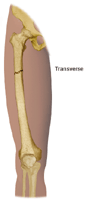
- Transverse. The break is in a straight line across the bone.
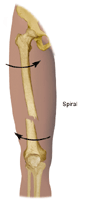
- Spiral. The break spirals around the bone; common in a twisting injury.
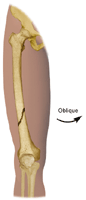
- Oblique. Diagonal break across the bone.
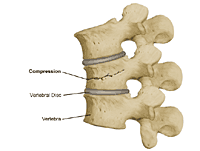
- Compression. The bone is crushed, causing the broken bone to be wider or flatter in appearance.
- Comminuted. The break is in three or more pieces.
Prevention & Risk Assessment
What causes a fracture?
Fractures occur when there is more force applied to the bone than the bone can absorb. Bones are weakest when they are twisted.
Breaks in bones can occur from falls, trauma, or as a result of a direct blow or kick to the body.
A child’s bone differs from adult bone in a variety of ways:
- A child’s bone heals much faster than an adult’s bone. The younger the child, the faster the healing occurs.
- Bones are softer in children and tend to buckle or bend rather than completely break.
- Children have open growth plates, also called epiphysis, located at the end of the long bones. This is an area where the bone grows. Injury to the growth plate can lead to limb length discrepancies or angular deformities.
What are the symptoms of a fracture?
The following are the most common symptoms of a fracture. However, each child may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
- Pain in the injured area
- Swelling in the injured area
- Obvious deformity in the injured area
- Difficulty using or moving the injured area in a normal manner
- Warmth, bruising, or redness in the injured area
The symptoms of a broken bone may resemble other conditions. Always consult your child’s doctor for a diagnosis.